Your laptop’s performance features limit you from running certain games or processes such as video editing on it.
What if I told you that you could get better performance from your laptop without buying a new one?
This is what overclocking does. Overclocking your laptop enables you to extract more performance from it than the manufacturer intended. Meaning if your laptop’s performance speed is 2.4 GHz, you can increase it to 3.0 GHz.

Be aware that overclocking is dangerous and can easily damage your laptop if it is not done correctly. However, if you can match the power and cooling demands of overclocking, you can enjoy the benefits without frying your laptop.
Here we’re going to show you how to overclock a laptop with an Intel processor and an AMD processor.
Disclaimer: Overclocking voids your laptop’s warranty. If you want to do it, make sure you understand your laptop’s limits; if not, contact a professional.
Overclocking works on the principle that your laptop’s CPU has a base clock that determines its performance speed. Most laptops perform at a speed of 1.7 – 4 GHz. Overclocking multiplies your base clock to achieve a higher performance speed than the one assigned to it by the manufacturer.
Table of Contents
How do you overclock a laptop with an Intel processor?

Most laptops today utilize Intel processors in their CPUs. So how would you overclock a laptop with this type of processor?
What do you require?
Not all Intel laptops can handle overclocking. If you do not have any of the following features, overclocking will fry your laptop.

.Before you can even think about overclocking, make sure your laptop has these features:
1. A CPU that is unlocked for overclocking
Intel has realized that there are computer hardware enthusiasts among their customers who tend to overclock their products. Recent CPU models released by Intel are overclock enabled. If your CPU has a ‘K’ or ‘X’ at the end, for example, core i7 9700K, it is unlocked for overclocking. To check the type of CPU you have, please follow these steps.
2. A motherboard that can handle overclocking
Z and X series motherboards have been unlocked for overclocking. You need this type of motherboard alongside an unlocked CPU. They are in stock at amazon if you’re using a desktop.
3. A cooling system
Overclocking prompts your laptop to work at higher speeds that demand a higher voltage supply, resulting in more heat production. Therefore, you will need a cooling system that carters for the extra heat produced.
There are numerous ways to overclock your Intel laptop (which I will mention later), but the safest way is to use Intel’s overclocking software: Intel® Extreme Tuning Utility (Intel® XTU).
Overclocking using Intel® Extreme Tuning Utility (Intel® XTU)
This software increases your laptop’s performance speed while maintaining a low temperature. First, download this program from this link, install and restart your computer.
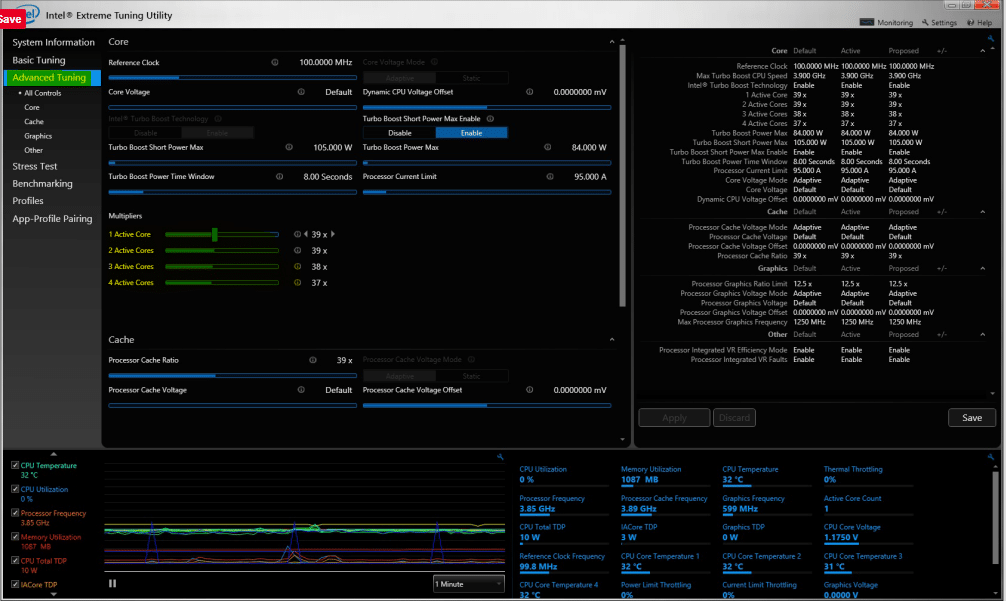
Before you begin the overclocking process, you need to assess your laptop’s performance. Under base tuning, click Benchmarking and then select Run benchmark.
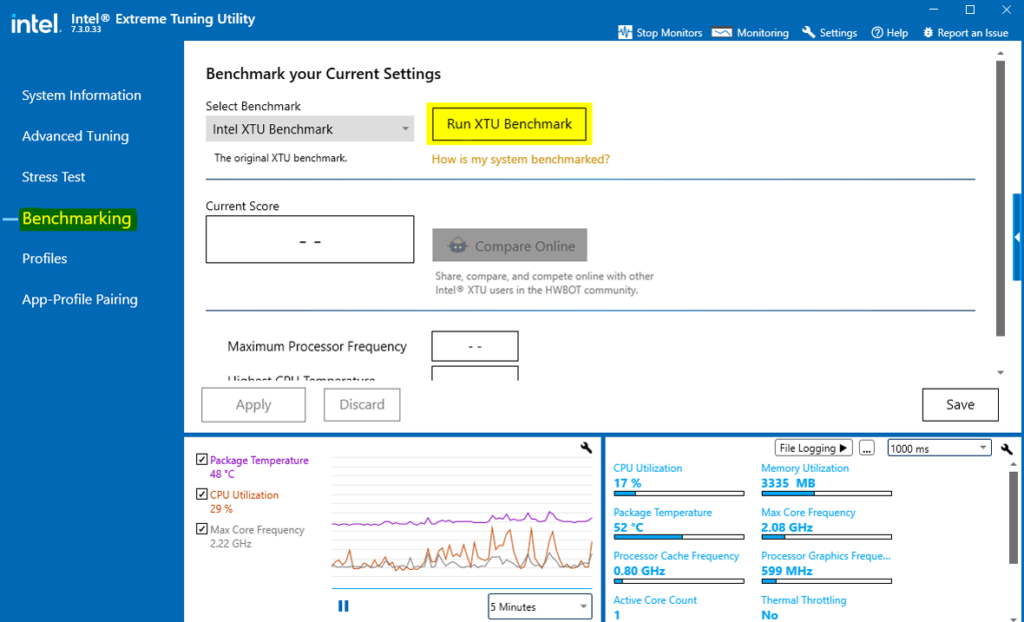
Under Current score, a value of how well your laptop is performing will be displayed. For example, under this score, you will see Processor Core Ratio and Processor Cache Ratio, increase these values to the maximum. Then run the benchmark once more.
You will notice that the score does not change, but the CPU core speed (XX GHz) will increase. Since you need your overall performance to increase, click on Advanced Tuning and click on All Controls. Here you will see Active Cores. Increase these values to the maximum. These are similar to the processor core and cache ratios in basic tuning.
When you check Turbo boost on your right, you should see an increased value for the performance speed.
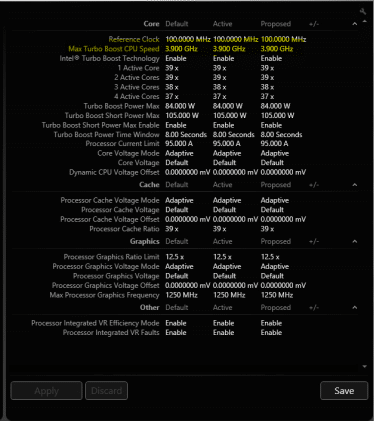
The next thing you adjust is Core Voltage and Processor Cache Voltage Offset. For these two, you subtract the voltage by, for example, 50mV from each one. You also need to increase your processor cache ratio to the maximum Click Apply to apply the changes you have made.
Now you want to see how these changes have affected the performance of your laptop. Go back to Benchmark and click on Run Benchmark. You should get a higher score than when you ran your first benchmark.
The maximum processor frequency should increase while the highest CPU temperature should decrease because you reduced the core voltage and cache voltage offset. Thus, this software enables you to get faster performance speeds for lower temperatures, a win-win situation.
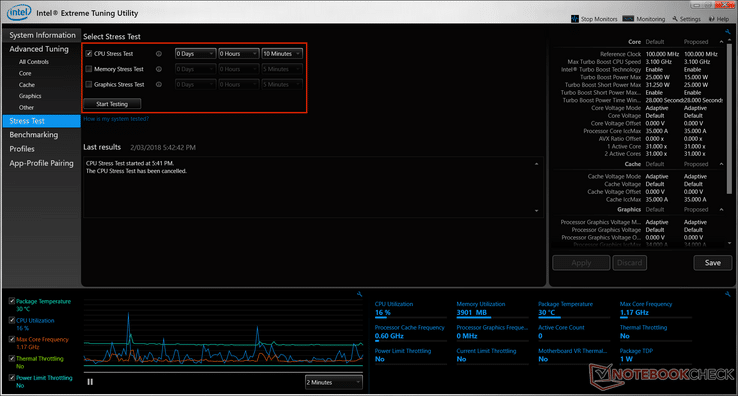
After this, you need to check the stability of your laptop after the changes. If it is not stable, it might crash or freeze. You do this by running a CPU Stress Test followed by memory and finally graphics test.
It should display Passed once each test is complete. This indicates your laptop is stable.
Other Overclocking Methods
You can overclock your computer by adjusting the BIOS settings. This is only enabled in certain laptop brands; you cannot overclock this way if you’re using HP or Dell. You can also use other software such as MSI Afterburner. These methods are risky and might lead to your laptop crashing or freezing.
How do you Overclock a Laptop with an AMD Processor?
If your laptop has an AMD processor instead of Intel, you’re in luck.

Unlike Intel processors, all AMD Ryzen processors come with an inbuilt overclock feature. Their site defines the limits to which you can overclock your laptop’s speed, voltage, etc., without causing damage to the motherboard. Overclocking a laptop with AMD processors requires two software: AMD µprof (the monitoring software) and Ryzen Controller (the overclocking software).
To download AMD µprof, go to this link. Scroll down until you see Download. Here you will see numerous links; click on the one that matches your operating system. It will take you to the download page, where you will click Accept, and your program will be downloaded.
Next, you need to download the Ryzen Controller that is built for overclocking all AMD Ryzen devices. Click here to download the Ryzen Controller.

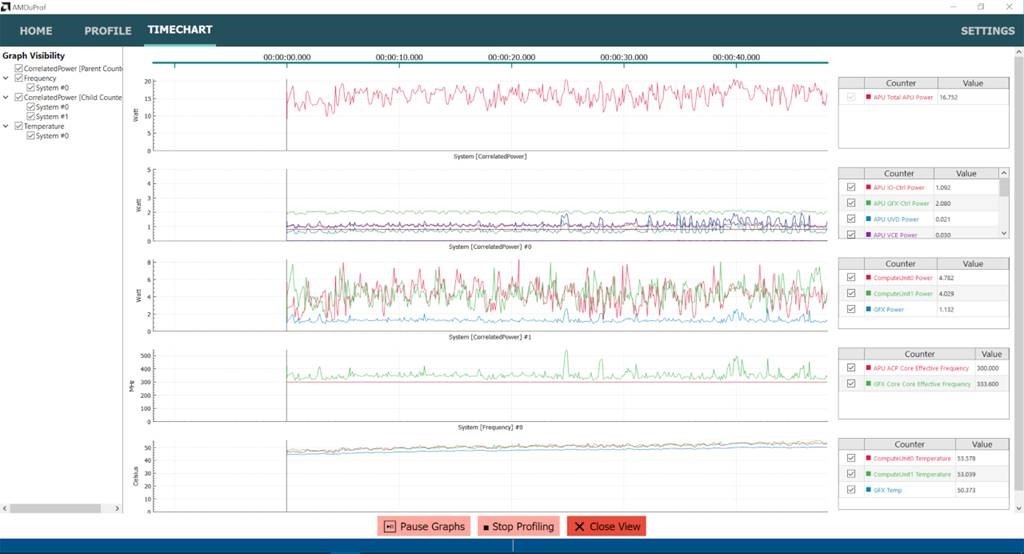
Now that you’ve downloaded both programs, go to downloads and install both programs. Once installed, open AMD µprof first and click on See what’s guzzling power on your system on the homepage.
This will take you to a new page to check all the boxes for power, frequency, temperature, P-state, and controllers. Then click Start Profile. It should display the performance this way.

This is like the benchmark for AMD laptops.
Before opening Ryzen Controller, make sure AMD µprof is running in the background.
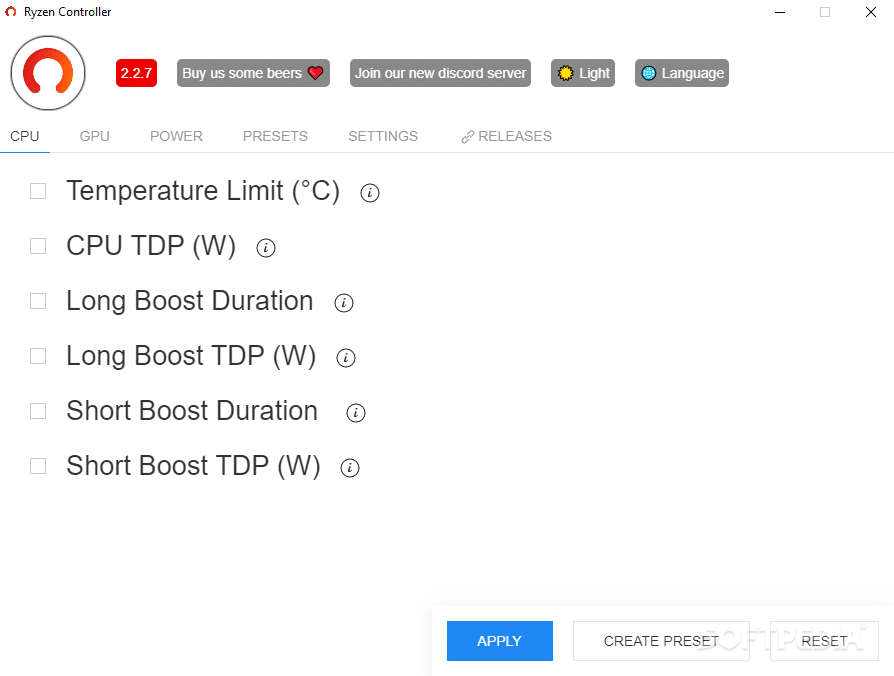
You can start overclocking by increasing the CPU TDP. This is the expected power consumption for your laptop. Before you do this, check the CPU ID (3500U, for example), and then go to the Ryzen website to check the limits to which you can set this CPU’s TDP. The website will give you the ranges, for example, 15-35W—do not go beyond the upper limit. Next, go back to Ryzen control and increase the CPU TDP maximum and minimum values.
Go to the GPU section to increase the performance speed. Here you increase the Minimum and Maximum Vega iGPU frequencies. You can also increase the minimum loss frequency of your CPU this way. Remember not to go beyond the limits stated on the Ryzen homepage. Click Apply to apply these changes.
Final words
Overclocking was mainly meant for desktops since you could buy hardware that supports overclocking. Recent software developments from both Intel and AMD enable you to milk every ounce of performance from your laptop. It is pretty risky as it voids your warranty, and you should only try it if you’re competent. Did you enjoy this tutorial? Inform us in the comments section if this information has been helpful to you.






Be the first to comment